Integrative Multiomics and Systems Biology of Common Human Diseases
Research in our lab employs integrative multiomics and systems biology approaches to understand the molecular networks underlying common cardiometabolic disorders such as coronary artery disease, diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, brain disorders such as traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease, and the connections between cardiometabolic disorders and brain disorders.
Our research is built upon the hypothesis that the complex interactions between genetic (i.e., DNA variants) and environmental risk factors (e.g., diets, environmental pollutants) perturb specific gene networks which in turn induce variations in disease susceptibility and therapeutic response.
By developling and applying integrative multiomics and systems biology approaches that leverage genetic, transcriptomics, epigenomic, metabolomic, microbiome, and phenotypic data from human and rodent populations, we aim to identify causal molecular networks and key regulators that contribute to the development of human complex diseases and further utilize the disease networks to guide therapeutics. Details of our research are here.
Our lab has developed Mergeomics and Pharmomics tools for muti-omics data integration and drug repurposing, respectively. We have also developed single cell and spatial transcriptomics analytical tools SCING for gene regulatory network modeling and JSTA for cell segmentation and cell type annotation. Details of these tools are here.
Our research has been generously supported by BreakthroughT1D and NIH NIDDK, NINDS, NIMH, NICHD, and NHLBI.
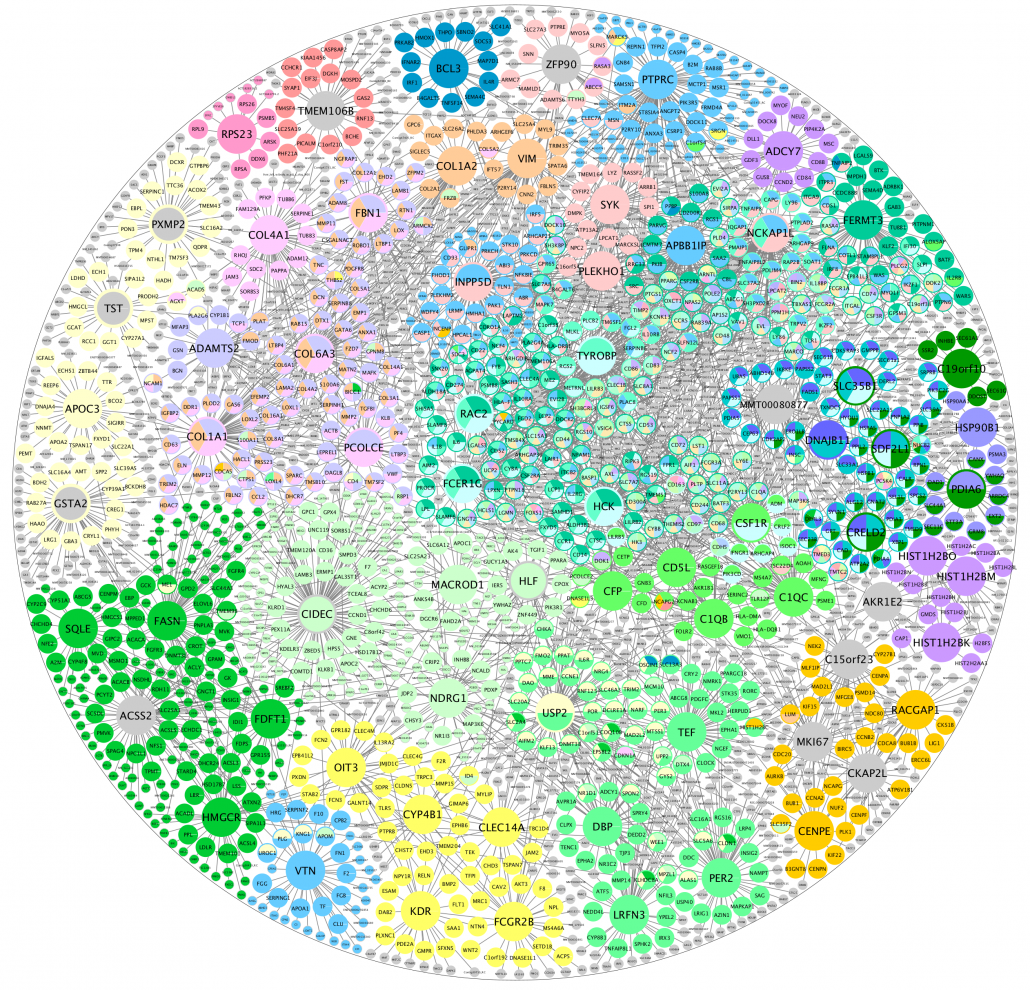
A disease network and key regulators. Figure credit: Jenny Cheng
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |